Track
Using large language models (LLMs) on local systems is becoming increasingly popular thanks to their improved privacy, control, and reliability. Sometimes, these models can be even more accurate and faster than ChatGPT.
We’ll show seven ways to run LLMs locally with GPU acceleration on Windows 11, but the methods we cover also work on macOS and Linux.
If you want to learn about LLMs from scratch, a good place to start is this course on Large Learning Models (LLMs).
Let’s start by exploring our first LLM framework.
1. Ollama
Ollama is the dominant ecosystem for running LLMs such as Llama 4, Mistral 3, and Gemma 3 locally.
Additionally, multiple applications accept an Ollama integration, which makes it an excellent tool for faster and easier access to language models on our local machine.
Ollama now offers full OpenAI API compatibility, making it a drop-in replacement for OpenAI's cloud service. Recent features include function calling, structured JSON output, Flash Attention for vision models, and 30% faster inference on Apple Silicon and AMD GPUs.
A. Installing Ollama
We can download Ollama from the download page.
Once we install it (using the default settings), the Ollama logo will appear in the system tray.
B. Running Ollama
We can download the Llama 3 model by typing the following terminal command:
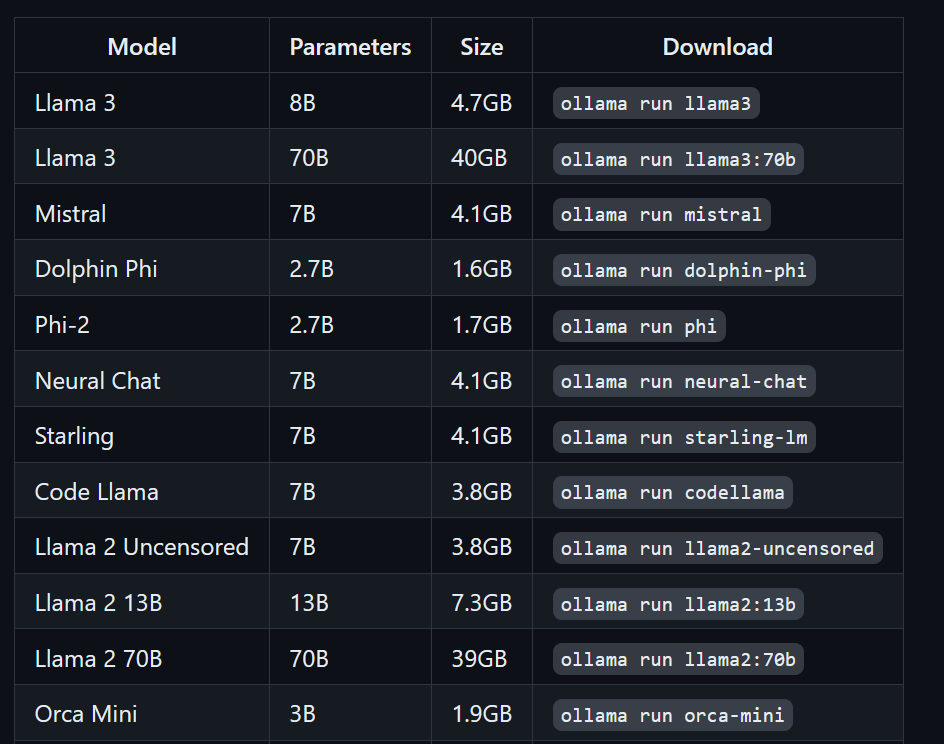
$ ollama run llama3Llama 3 is now ready to use! Below, we see a list of commands we need to use if we want to use other LLMs:
C. Running custom models
To access models that have already been downloaded and are available in the llama.cpp folder, we need to:
- Go to the llama.cpp folder using the
cdcommand.
$ cd C:/Repository/GitHub/llama.cpp- Create a filename called
Modelfileand add the line"FROM ./Nous-Hermes-2-Mistral-7B-DPO.Q4_0.gguf".
$ echo "FROM ./Nous-Hermes-2-Mistral-7B-DPO.Q4_0.gguf" > Modelfile- Build the model by providing the model’s name.
$ ollama create NHM-7b -f Modelfile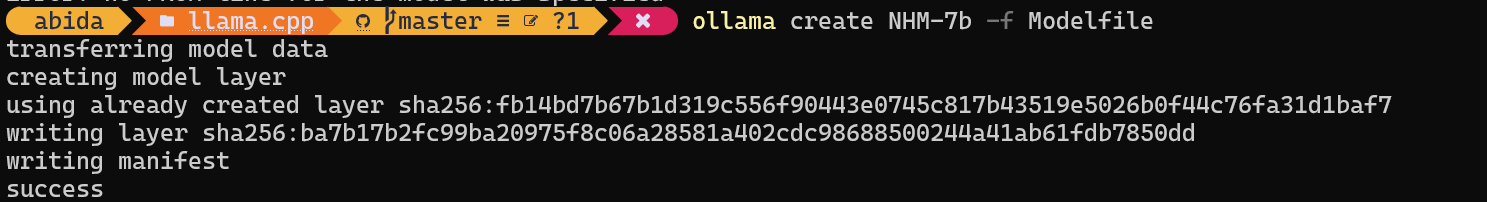
- Run the NHM-7b model.
$ ollama run NHM-7b- Use it as any other chat application.
With this method, we can download any LLM from Hugging Face with the .gguf extension and use it in the terminal. If you want to learn more, check out this course on Working with Hugging Face.
2. LM Studio
LM Studio is an all-in-one workbench for running LLMs locally and offers fine-tuning natively. Beyond that, it supports multiple concurrent models, speculative decoding (1.5x-3x faster tokens), and document RAG integration.
A. Installation
We can download the installer from LM Studio’s home page.
Once the download is complete, we install the app with default options.
Finally, we launch LM Studio!
B. Downloading the model
We can download any model from Hugging Face using the search function.
In our case, we'll download the smallest model, Google’s Gemma 2B Instruct.
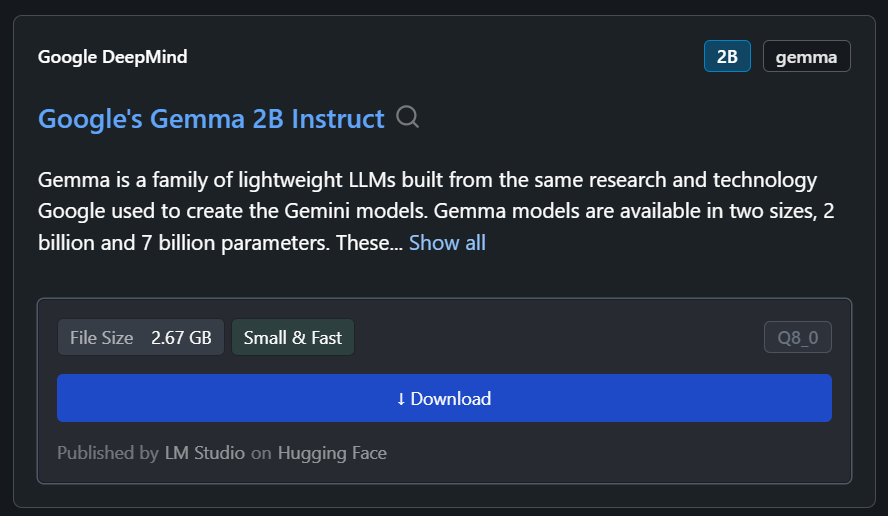
C. Generating the response
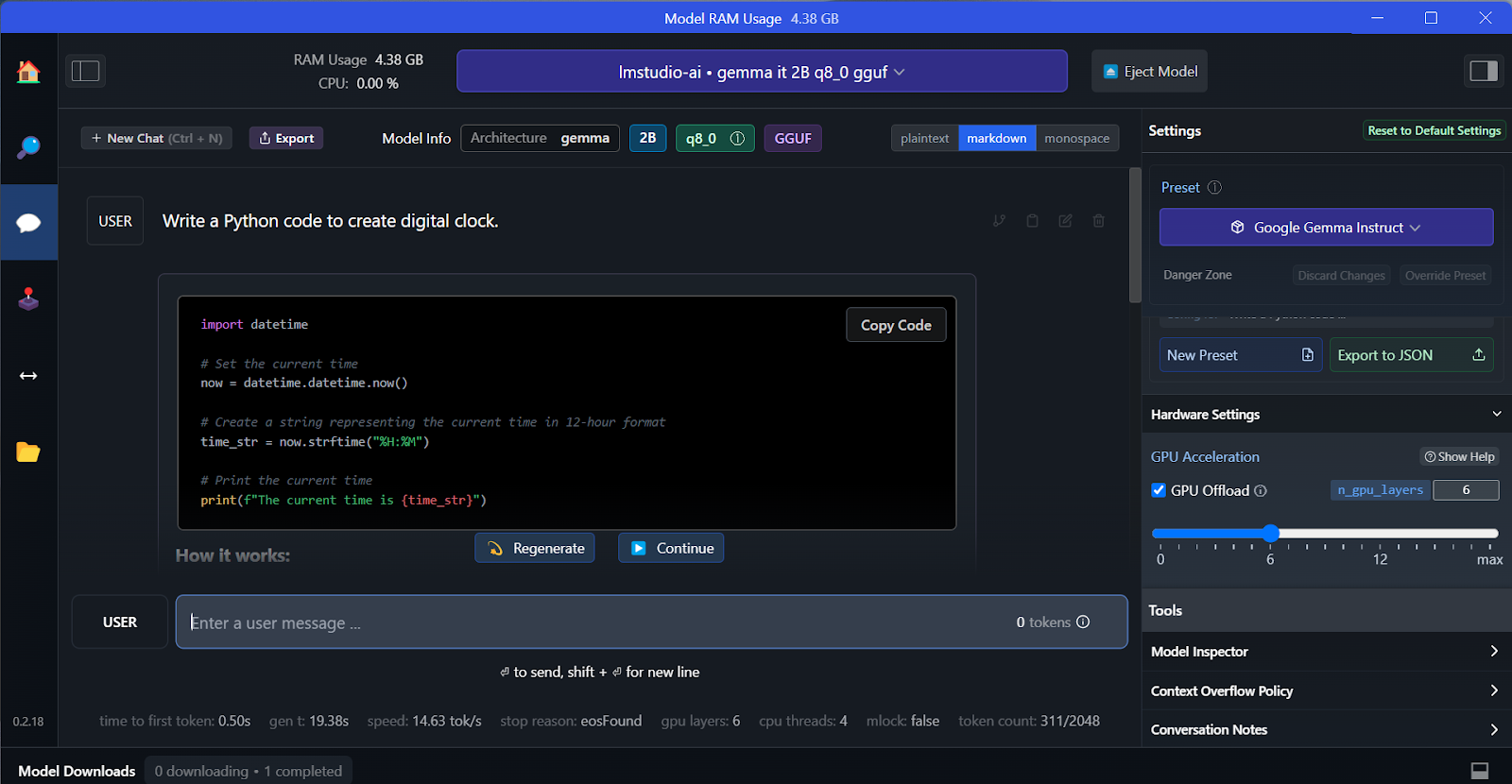
We can select the downloaded model from the drop-down menu at the top and chat with it as usual. LM Studio offers more customization options than GPT4All.
D. Local inference server
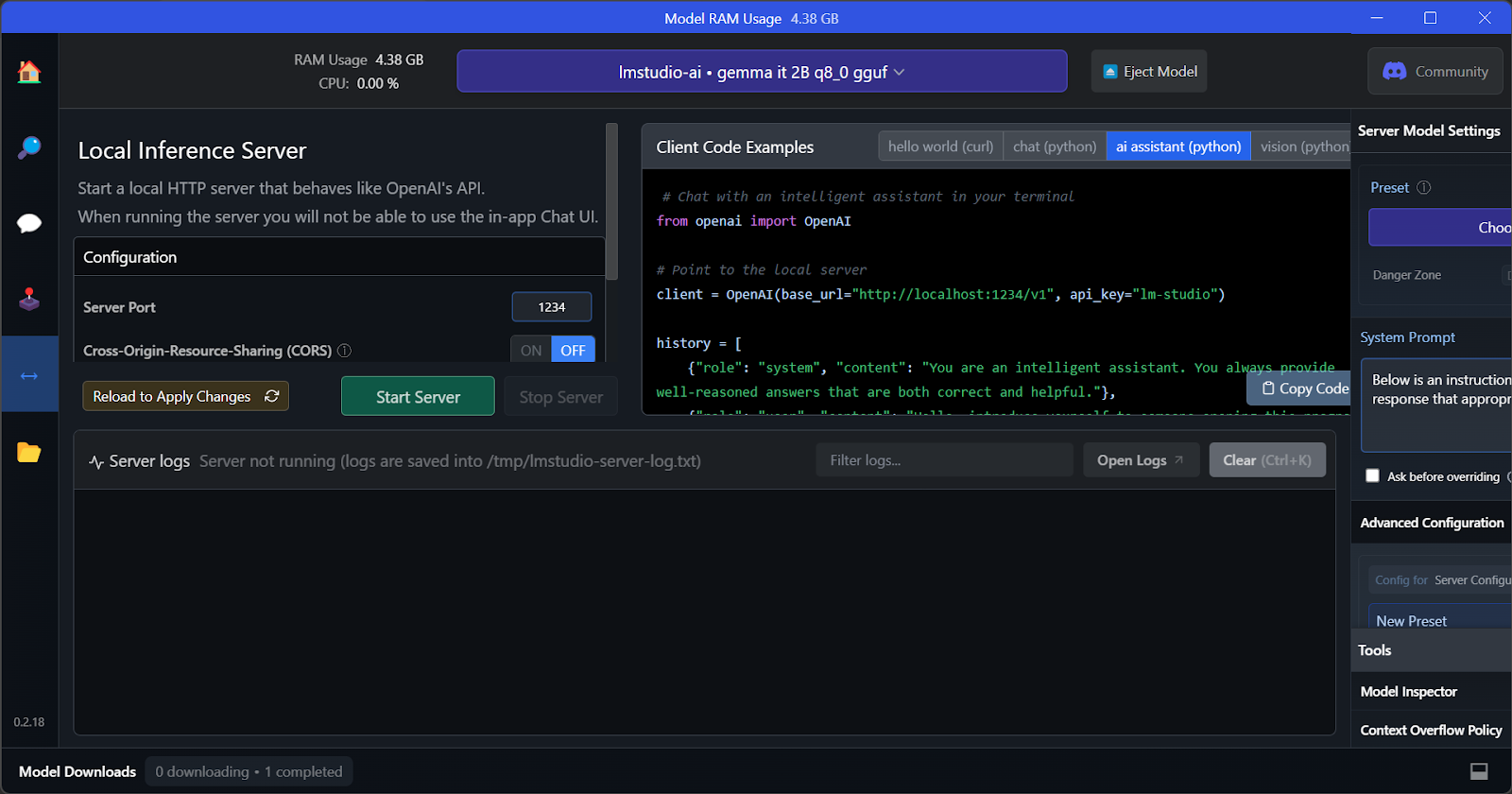
Like GPT4All, we can customize the model and launch the API server with one click. To access the model, we can use the OpenAI API Python package, CURL, or directly integrate with any application.
E. Using multiple models
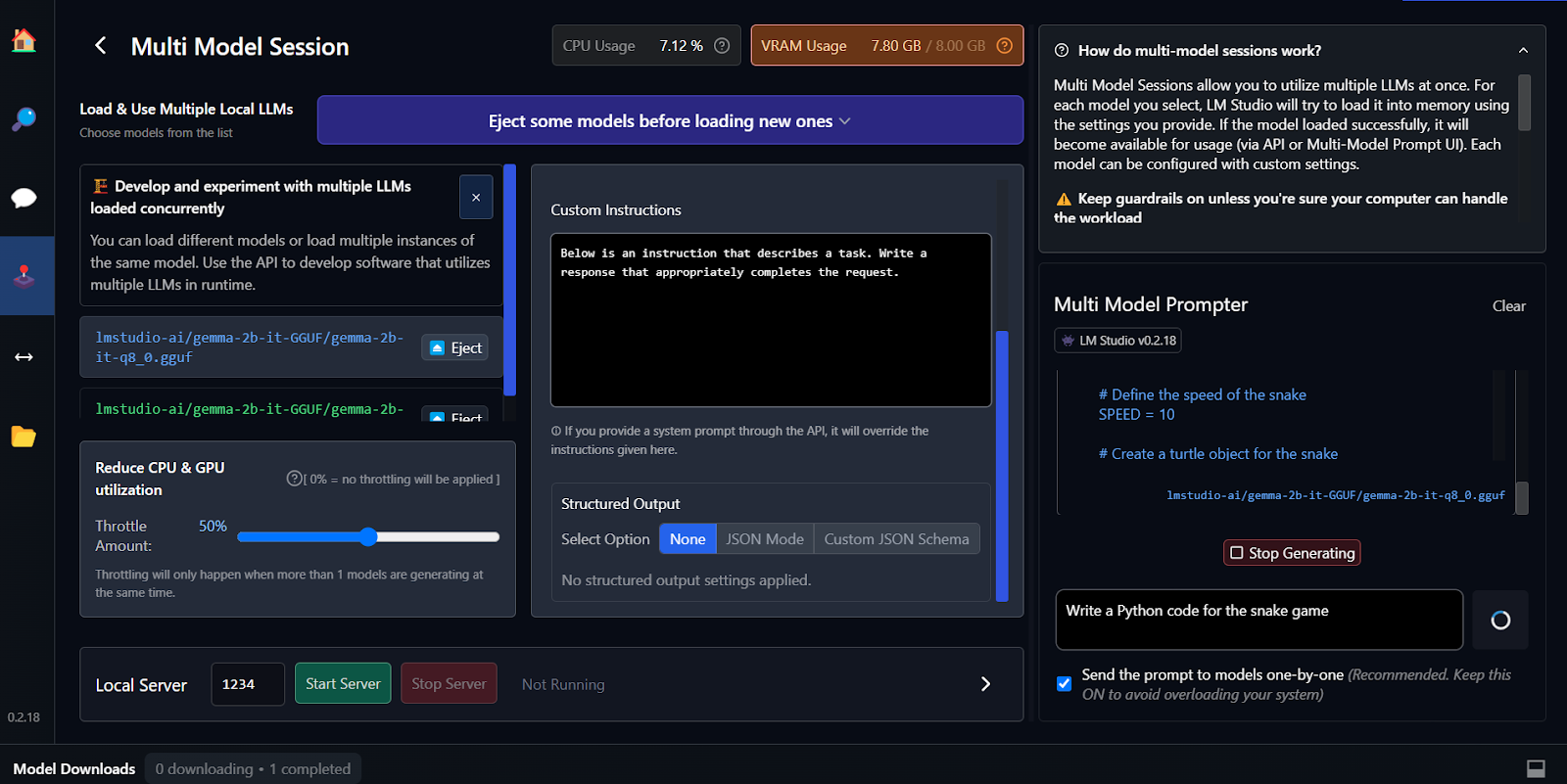
The key feature of LM Studio is that it offers the option to run and serve multiple models at once. This allows users to compare different model results and use them for multiple applications. In order to run multiple model sessions, we need a high GPU VRAM.
Fine-tuning is another way of generating context-aware and customized responses. You can learn to fine-tune your Google Gemma model by following the tutorial Fine Tuning Google Gemma: Enhancing LLMs with Customized Instructions. You'll learn to run inference on GPUs/TPUs and fine-tune the latest Gemma 7b-it model on a role-play dataset.
3. vLLM
vLLM is an open-source inference engine for running LLMs at production scale. Unlike Ollama or LM Studio, vLLM prioritizes throughput and latency for multi-user scenarios.
Its core innovation is PagedAttention, which manages GPU memory like virtual memory, reusing small pages instead of reserving massive blocks, combined with continuous batching. Real benchmarks show vLLM delivering 793 tokens per second on Llama 70B versus Ollama's 41 tokens per second under concurrent load.
vLLM also supports tensor parallelism across GPUs, prefix caching, and multi-LoRA batching for serving fine-tuned variants simultaneously.
A. Installation
On Mac and Linux, vLLM can be easily installed using pip.
On Linux with CUDA 11.8+:
pip install vllmOn macOS with Apple Silicon:
python3.11 -m venv vllm_env
source vllm_env/bin/activate
pip install vllmThere is no official support for Windows at the moment. However, workarounds via WSL2 or Docker exist.
B. Running Models
Start the OpenAI-compatible server:
vllm serve meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf --port 8000 --gpu-memory-utilization 0.9For 70B models on multiple GPUs:
vllm serve meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf --tensor-parallel-size 2 --port 8000For batch processing in Python:
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
llm = LLM(model="meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", dtype="bfloat16")
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.8, max_tokens=256)
outputs = llm.generate(["Write hello world", "Explain AI"], sampling_params)C. Running Inference
To query, use the OpenAI SDK:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(base_url='http://localhost:8000/v1', api_key='any')
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model='meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf',
messages=[{'role': 'user', 'content': 'What is ML?'}],
max_tokens=200
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)Another option is to run it via cURL:
curl http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model": "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}]}'Choose vLLM for production APIs serving hundreds of concurrent users; use Ollama for local development.
4. Jan
One of the most popular and best-looking local LLM applications is Jan. It is a privacy-first alternative for ChatGPT.
A. Installation
We can download the installer from Jan.ai.
Once we install the Jan application with default settings, we’re ready to launch the application.
B. Importing the model
When we covered GPT4All and LM Studio, we already downloaded two models. Instead of downloading another one, we'll import the ones we already have by going to the model page and clicking the Import Model button.
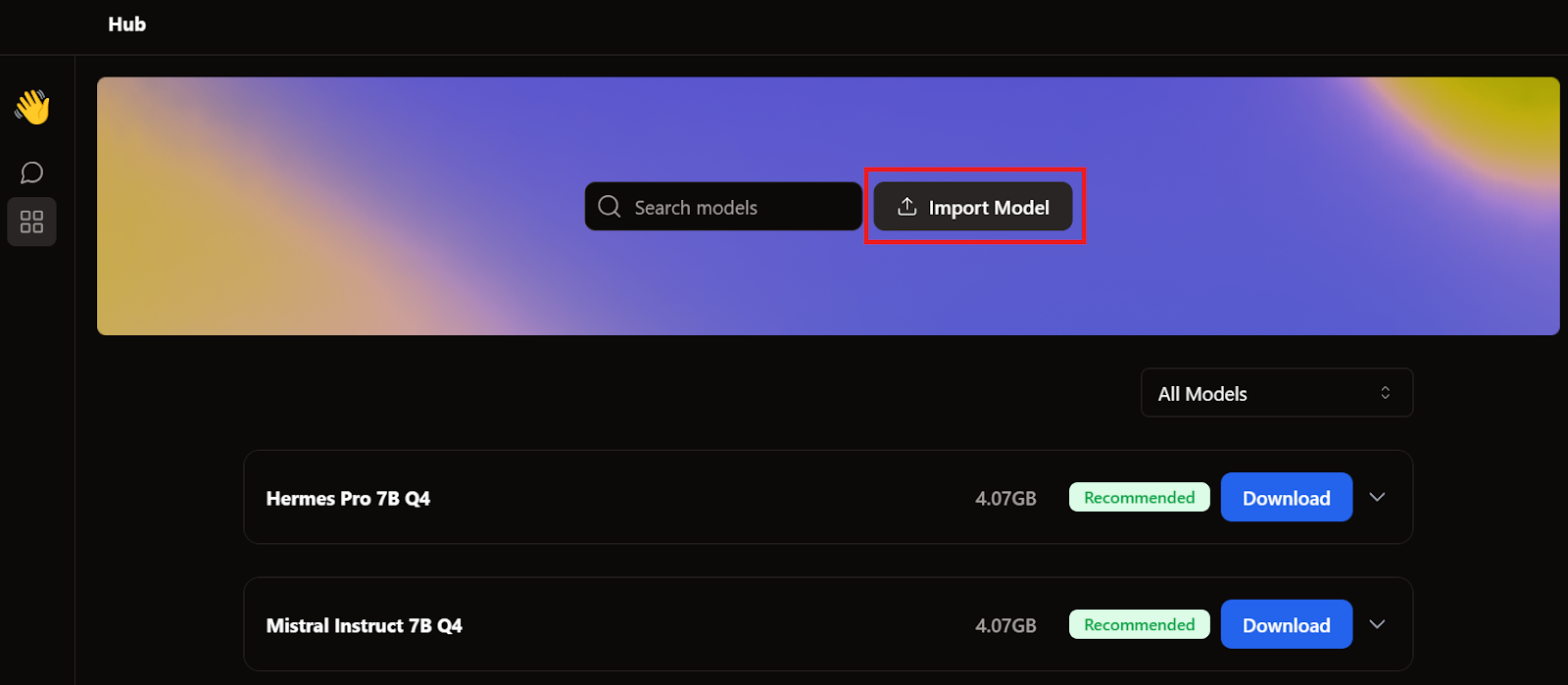
Then, we go to the applications directory, select the GPT4All and LM Studio models, and import each.
- GPT4All: "C:/Users/<user_name>/AppData/Local/nomic.ai/GPT4All/"
- LM Studio: "C:/Users/<user_name>/.cache/lm-studio/models"
C. Accessing the local models
To access the local models, we go to the chat user interface and open the model section in the right panel.
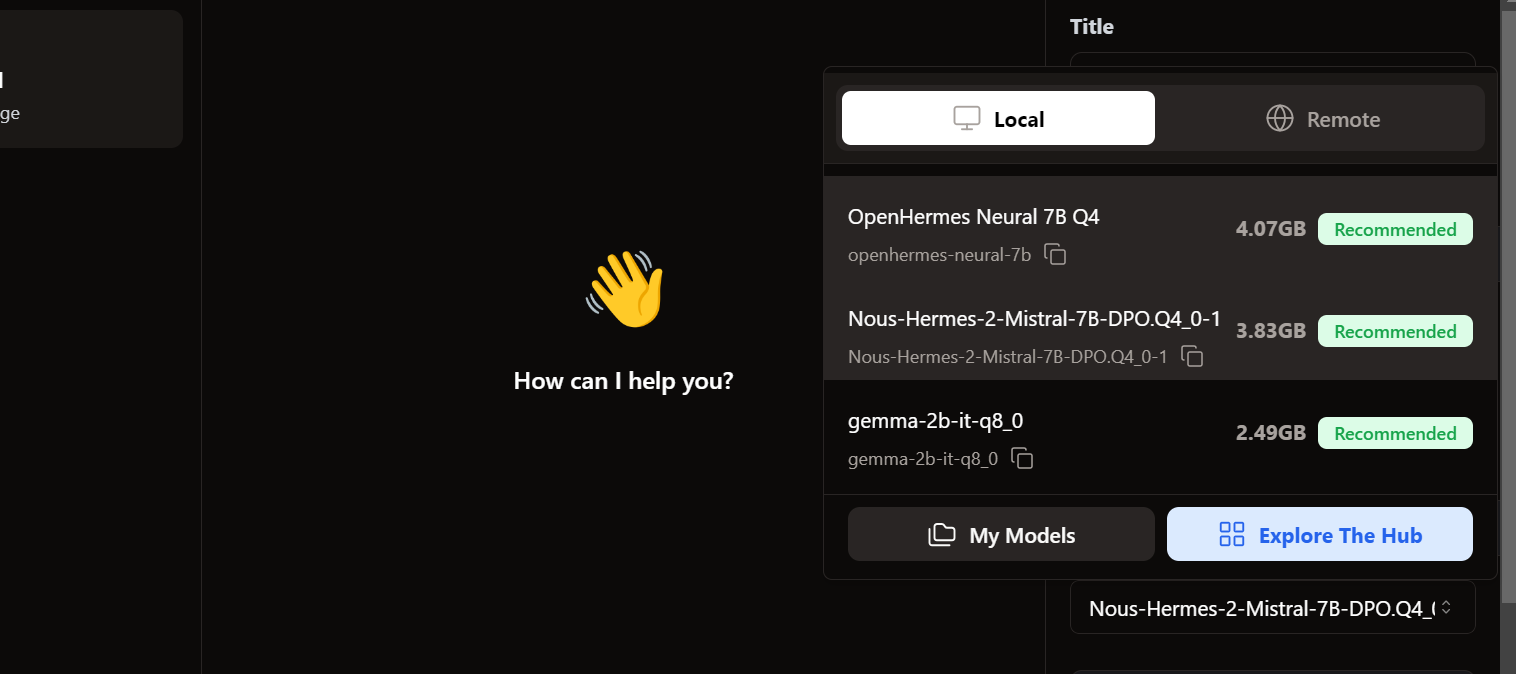
We see our imported models are already there. We can select the one we want and start using it immediately!
D. Generating the response
The response generation is very fast. The user interface feels natural, similar to ChatGPT, and does not slow down your laptop or PC.
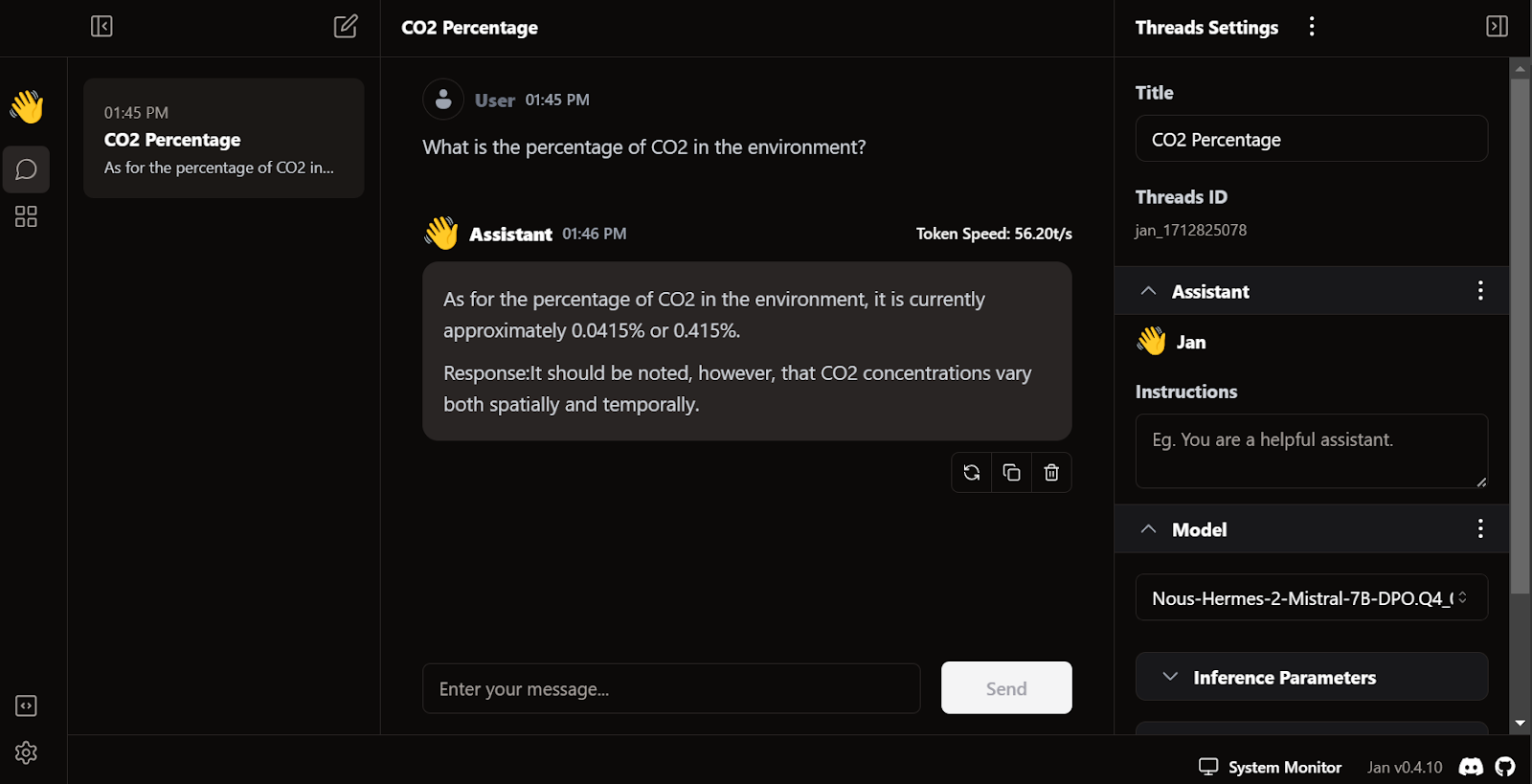
Jan's unique feature is that it allows us to install extensions and use proprietary models from OpenAI, MistralAI, Groq, TensorRT, and Triton RT.
E. Local API server
Like LM Studio, we can also use Jan as a local API server. It provides more logging capabilities and control over the LLM response, and integrates OpenAI, Mistral AI, Groq, Claude, and DeepSeek via simple API key setup in the settings.
5. llama.cpp
Another popular open-source LLM framework is llama.cpp. It's written purely in C/C++, which makes it fast and efficient.
Many local and web-based AI applications are based on llama.cpp. Thus, learning to use it locally will give you an edge in understanding how other LLM applications work behind the scenes.
A. Downloading the llama.cpp
First, we need to go to our project directory using the cd command in the shell—you can learn more about the terminal in this Introduction to Shell course.
Then, we clone all the files from the GitHub server using the command below:
$ git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp.gitB. Using MakeFile on Windows
The make command line tool is available by default in Linux and MacOS. For Windows, however, we need to take the following steps:
- Download the latest w64devkit Fortran version of w64devkit for Windows.
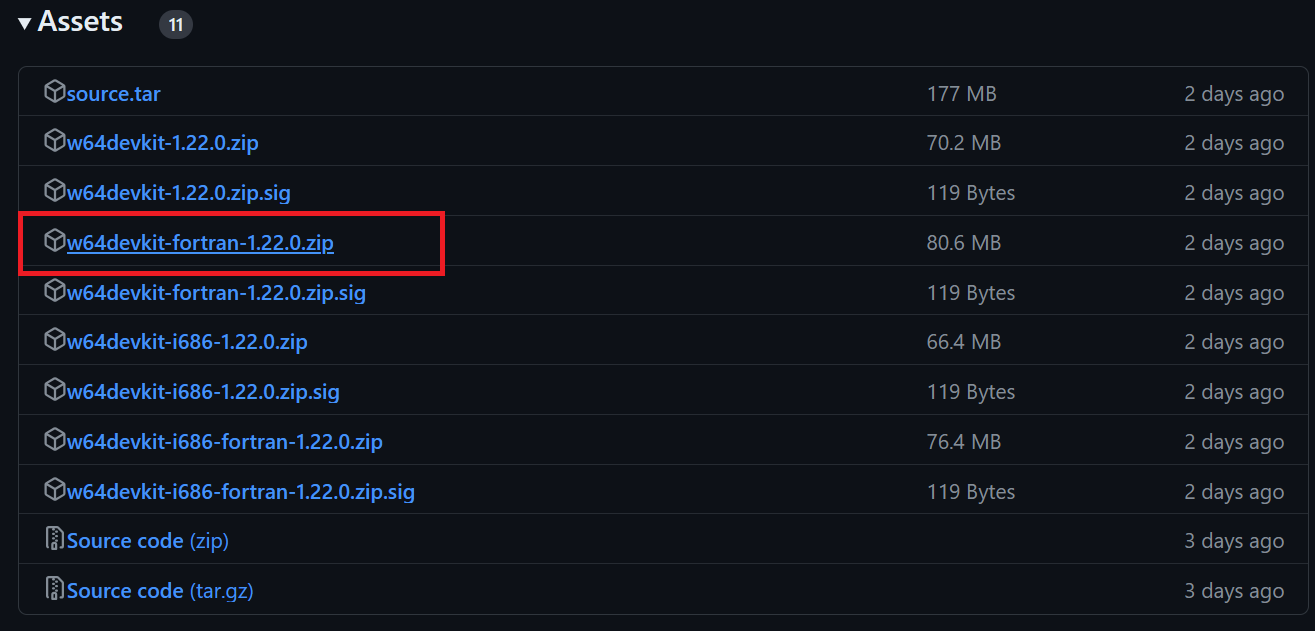
- Extract w64devkit on our local directory.
- In the main folder, we need to find the file w64devkit.exe and run it.
- Use the
$ cd C:/Repository/GitHub/llama.cppcommand to access the llama.cpp folder. - Type
$ makeand press Enter to install llama.cpp.
B. Starting the llama.cpp’s WebUI server
After we complete the installation, we run the llama.cpp web UI server by typing out the command below. (Note: We’ve copied the model file from the GPT4All folder to the llama.cpp folder so we can easily access the model).
$ ./server -m Nous-Hermes-2-Mistral-7B-DPO.Q4_0.gguf -ngl 27 -c 2048 --port 6589
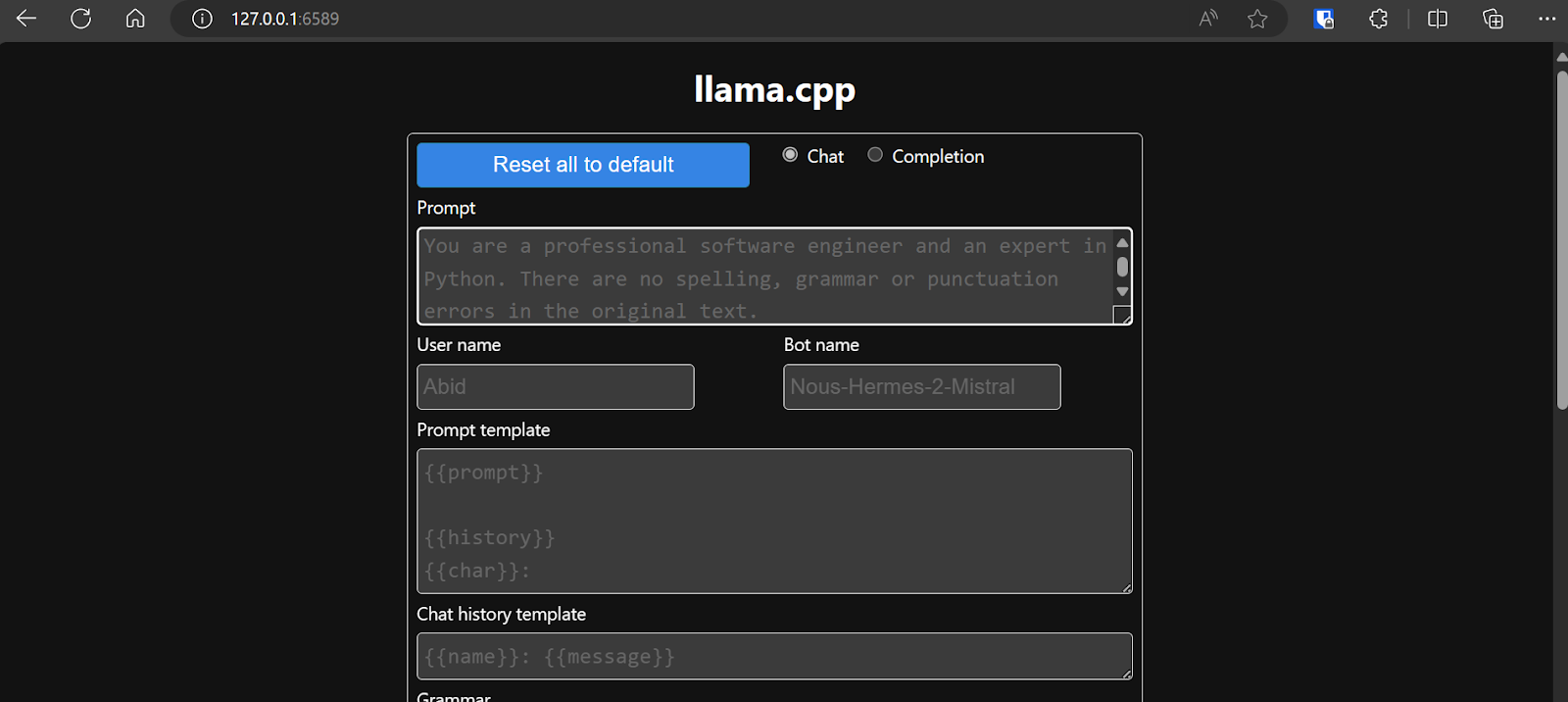
The web server is running at http://127.0.0.1:6589/. You can copy this URL and paste it into your browser to access the llama.cpp web interface.
Before interacting with the chatbot, we should modify the settings and model’s parameters.
 Check out this llama.cpp tutorial if you want to learn more!
Check out this llama.cpp tutorial if you want to learn more!
D. Generating the response
The response generation is slow because we run it on CPU, not GPU. We must install a different version of llama.cpp to run it on GPU.
$ make LLAMA_CUDA=1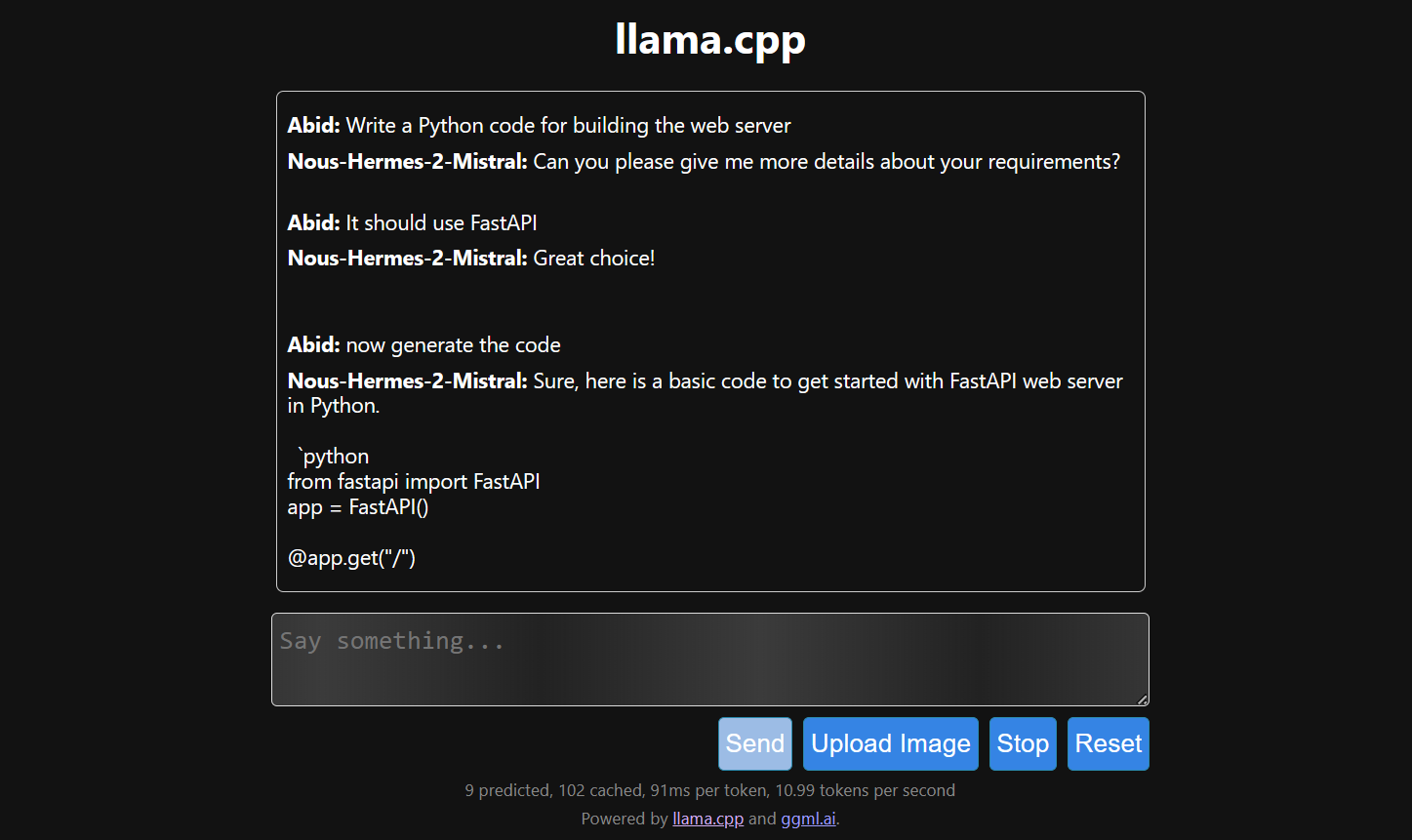
6. llamafile
If you find llama.cpp a bit too complex, try llamafile. This framework simplifies LLMs for both developers and end-users by combining llama.cpp with Cosmopolitan Libc into a single-file executable. It removes all the complexities associated with LLMs, making them more accessible.
A. Downloading the model file
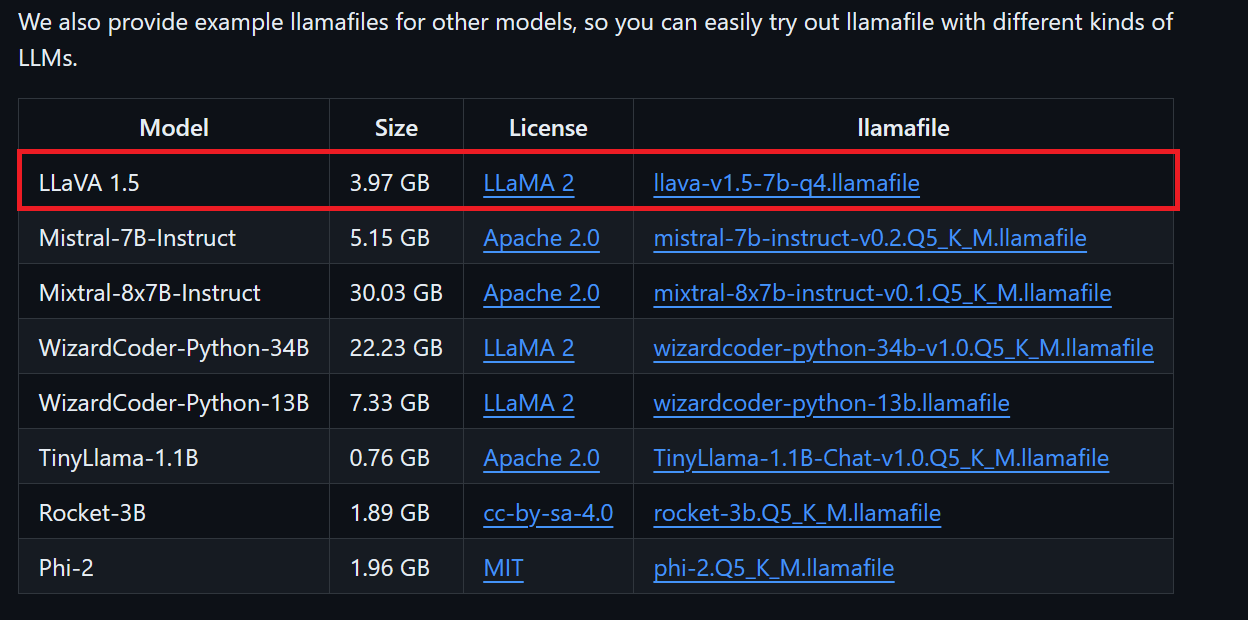
We can download the model file we want from llamafile’s GitHub repository.
We'll download LLaVA 1.5 because it can also understand images.
B. Making changes for Windows
Windows users must add .exe to file names in the terminal. To do this, right-click the downloaded file and select Rename.

C. Running the LlamaFile
We first go to llamafile directory by using the cd command in the terminal. Then, we run the command below to start the llama.cpp web server.
$ ./llava-v1.5-7b-q4.llamafile -ngl 9999The web server uses the GPU without requiring you to install or configure anything.
It'll also automatically launch the default web browser with the llama.cpp web application running. If it doesn’t, we can use the URL http://127.0.0.1:8080/ to access it directly.
D. Generating the response
After we settle on the model’s configuration, we can start using the web application.
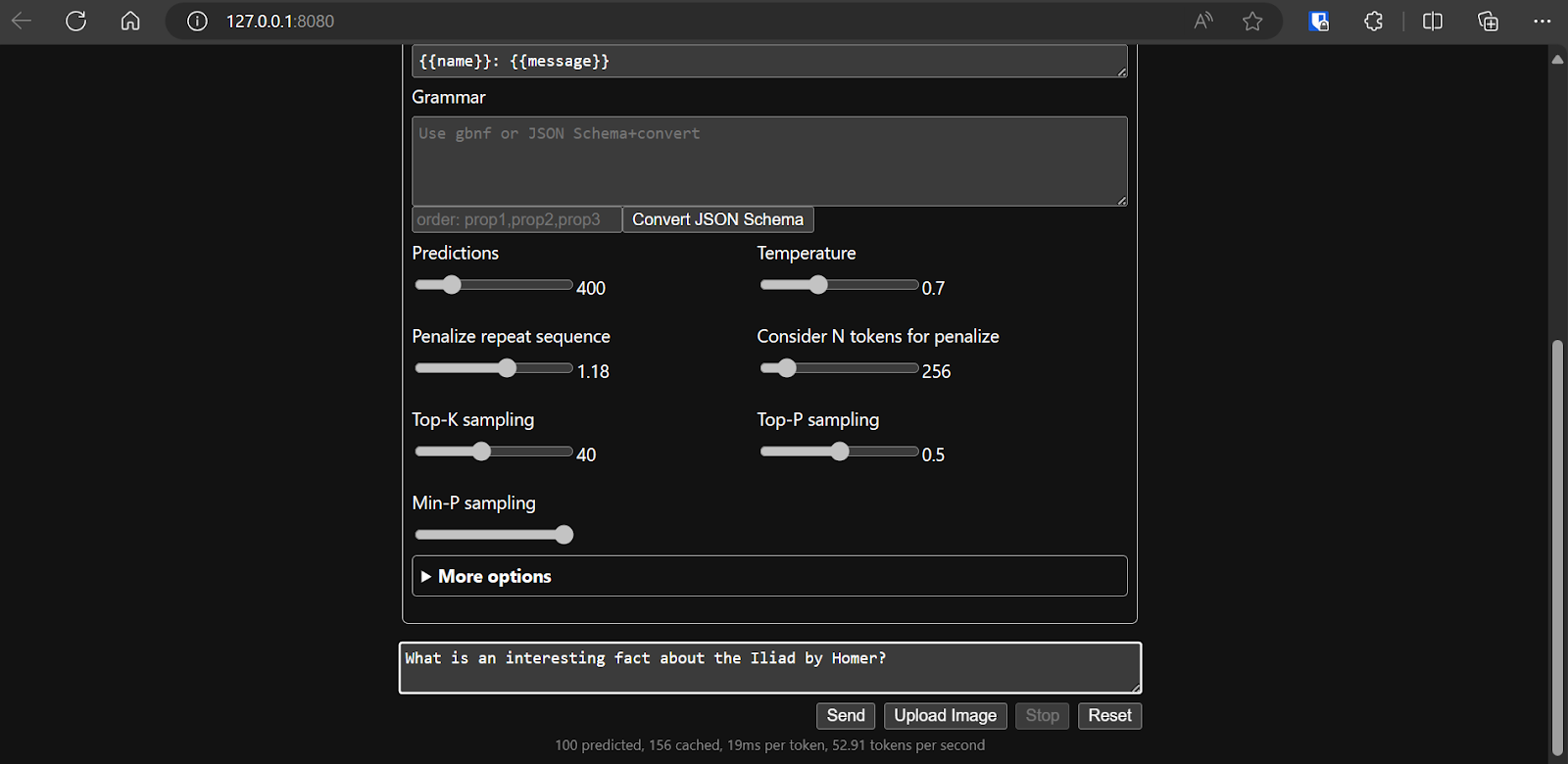
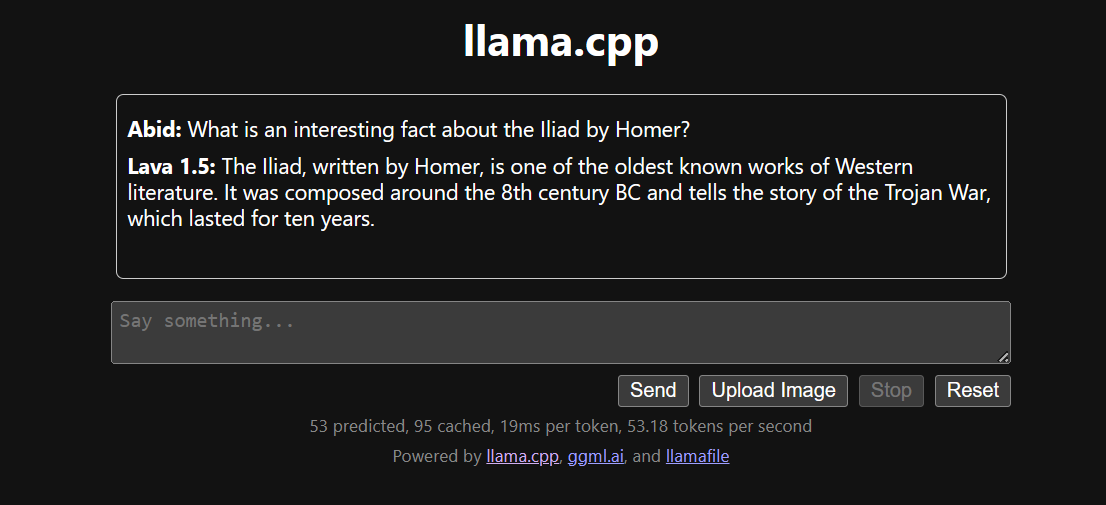
Running the llama.cpp using the llamafile is easier and more efficient. We generated the response with 53.18 tokens/sec (without llamafile, the rate was 10.99 tokens/sec).
Conclusion
Installing and using LLMs locally can be a fun and exciting experience. We can experiment with the latest open-source models on our own, enjoy privacy, control, and an enhanced chat experience.
Using LLMs locally also has practical applications, such as integrating it with other applications using API servers and connecting local folders to provide context-aware responses. In some cases, it is essential to use LLMs locally, especially when privacy and security are critical factors.
You can learn more about LLMs and building AI applications by following these resources:

As a certified data scientist, I am passionate about leveraging cutting-edge technology to create innovative machine learning applications. With a strong background in speech recognition, data analysis and reporting, MLOps, conversational AI, and NLP, I have honed my skills in developing intelligent systems that can make a real impact. In addition to my technical expertise, I am also a skilled communicator with a talent for distilling complex concepts into clear and concise language. As a result, I have become a sought-after blogger on data science, sharing my insights and experiences with a growing community of fellow data professionals. Currently, I am focusing on content creation and editing, working with large language models to develop powerful and engaging content that can help businesses and individuals alike make the most of their data.