Curso
The CORREL() function in Excel is a powerful statistical tool that helps users determine the relationship between two sets of data. By calculating the correlation coefficient, you can quickly assess whether two variables move together, move in opposite directions, or have no relationship at all.
In this article, I'll will walk you through how to use the CORREL() function in Excel, along with its syntax, and some examples. It's a good starting point for other things, also, as you will see, like regression and things that happen in finance, such as when working with stock returns and interest rates.
What Is the CORREL() Function in Excel?
The CORREL() function in Excel measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. The result, known as the correlation coefficient or, more exactly, the Pearson correlation coefficient, ranges from -1 to 1:
- 1 indicates a perfect positive correlation
- -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation
- 0 indicates no linear correlation
This function is commonly used to quantify relationships—for instance, a strong negative correlation (close to -1) between interest rates and bond prices, or a strong positive one (close to 1) between advertising spend and revenue.
Excel CORREL() Syntax and Arguments
Before using the CORREL() function, it's important to understand its syntax and required arguments. The function requires two ranges of data as input.
=CORREL(array1, array2)-
array1: The first range of values -
array2: The second range of values
Both arrays must have the same number of data points. If they do not, CORREL() will return a #N/A error.
How to Use CORREL() in Excel
To use the CORREL() function in Excel, follow these steps:
-
Enter your two data sets in separate columns.
-
Click on the cell where you want the correlation coefficient to appear.
-
Type the
CORREL()formula, referencing your data ranges. -
Press Enter to display the result.
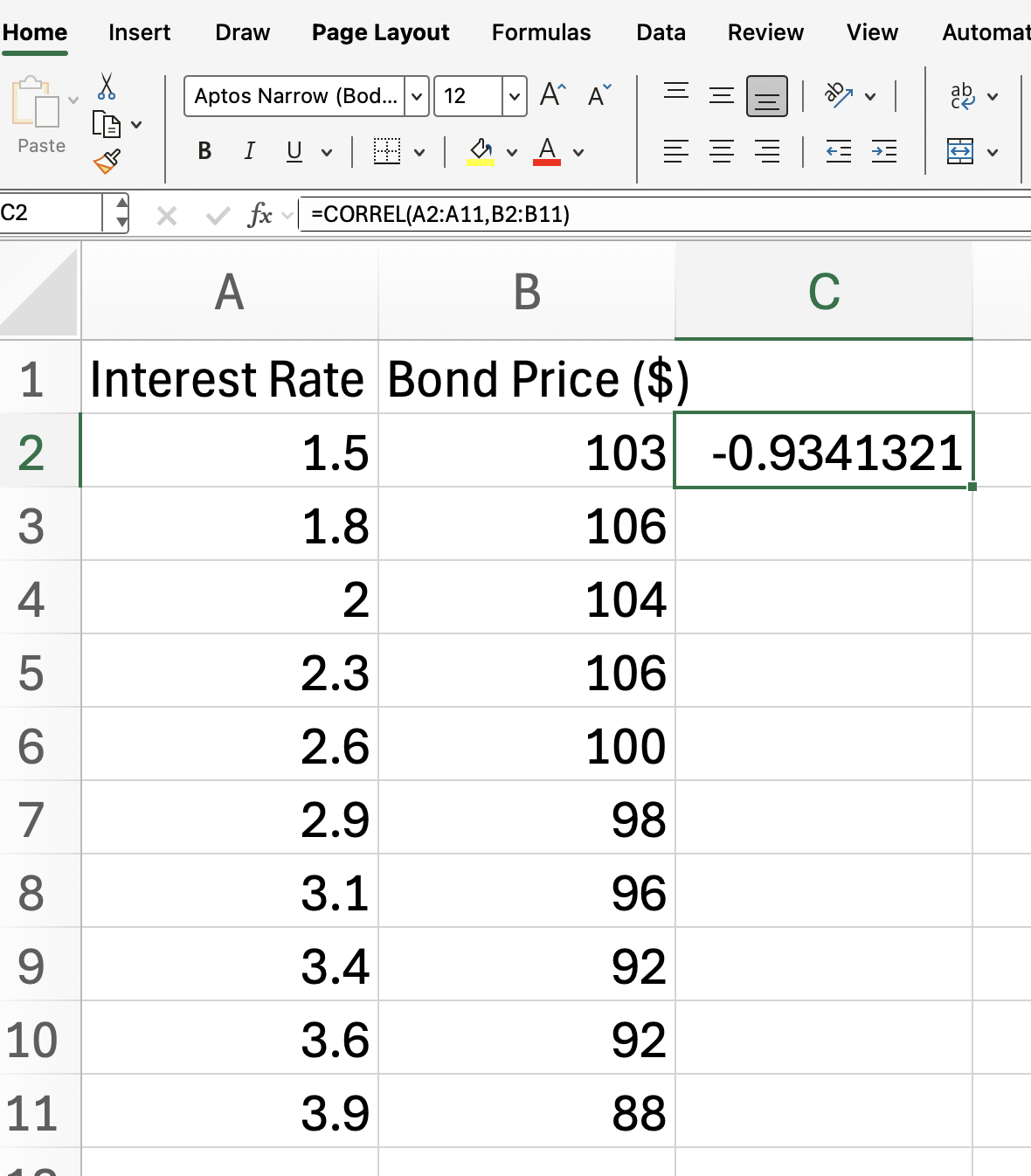
For example, if your data is in columns A and B from rows 2 to 11:
=CORREL(A2:A11, B2:B11)Our formula returns the correlation coefficient between the two data sets.
We expect get a result close to -1, indicating a strong negative correlation between interest rates and bond prices, as this aligns with financial theory, since as interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall.
Interpreting CORREL() Results in Excel
After calculating the correlation coefficient, it's important to interpret the result correctly. The value you get from CORREL() will fall between -1 and 1:
- Values close to 1: Strong positive correlation (as one variable increases, so does the other)
- Values close to -1: Strong negative correlation (as one variable increases, the other decreases)
- Values close to 0: Little or no linear relationship
Keep in mind that correlation does not imply causation. A high correlation coefficient simply indicates a relationship, not that one variable causes the other to change.
Common Errors with CORREL()
When using the CORREL() function in Excel, you may encounter some common errors. Understanding these can help you troubleshoot issues quickly.
-
N/Aerror: Occurs if the two arrays have different numbers of data points -
DIV/0!error: Happens if either array has less than two data points or if the standard deviation of either array is zero -
VALUE!error: Appears if non-numeric values are included in the data ranges
If you make sure that your data ranges are equal in length and contain only numeric values, I think you will avoid all of these errors.
Conclusion
The CORREL() function in Excel is an essential tool for analyzing the relationship between two data sets. Once you are comfortable using the CORREL() function, you may want to explore other statistical functions in Excel. Functions like COVARIANCE.P() and LINEST() are very useful for what they do. And make sure to take our Data Analysis in Excel course to keep learning.
Advance Your Career with Excel
Gain the skills to maximize Excel—no experience required.

I'm a data science writer and editor with contributions to research articles in scientific journals. I'm especially interested in linear algebra, statistics, R, and the like. I also play a fair amount of chess!